🥗 Optimal Foods for Fat Reduction, Weight Management, and Balanced Daily Nutrition
A balanced diet should include foods rich in micronutrients, fiber-containing carbohydrates, lean protein sources, and healthy fats. The primary objective is to expend more calories than are consumed each day to achieve a caloric deficit while ensuring the body receives essential vitamins and minerals.
Important Food Categories for Fat Loss
- Vegetables and Fruits
- Oranges, Spinach, Broccoli, Berries, kale, apples are examples.
- Contain vitamins A, C, and K, rich in antioxidants, and fibre are the benefits.
- Carbohydrate Complexity
- sweet potatoes, oats, quinoa, brown rice, whole-grain bread are some examples.
- Stable blood sugar levels and slow-releasing energy are benefits of it.
- Maintaining Hydration
- Water is very important and necessary for digestion, metabolism, and the removal of toxins.
- Drink water at least 2.5 to 3 litres daily but It also depends on your daily activities or routine.
- Nutritious Fats
- fatty fish, avocado, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are best examples.
- Promote vitamin absorption, brain health, and hormone production are benefits.
- Lean Proteins
- Fish, Eggs, Turkey, tofu, Chicken breast, lentils are best examples of lean proteins.
- Increase metabolism, build and maintain muscle mass, and enhance satisfaction are benefits of it.

Visualize nutrients in Table:
| Food Category | Examples | Benefits |
| Vegetables and Fruits | Oranges, Spinach, Broccoli, Berries, kale, apples | Contain vitamins A, C, and K, rich in antioxidants, and fibre |
| Carbohydrate Complexity | sweet potatoes, oats, quinoa, brown rice, whole-grain bread | Stable blood sugar levels and slow-releasing energy |
| Maintaining Hydration | Water | Necessary for digestion, metabolism, and the removal of toxins |
| Nutritious Fats | fatty fish, avocado, nuts, seeds, olive oil | Promote vitamin absorption, brain health, and hormone production |
| Lean Proteins | Fish, Eggs, Turkey, tofu, Chicken breast, lentils | Increase metabolism, build and maintain muscle mass, and enhance satisfaction |
| Water Intake Recommendation | 2.5 to 3 litres daily | Depends on daily activities or routine |
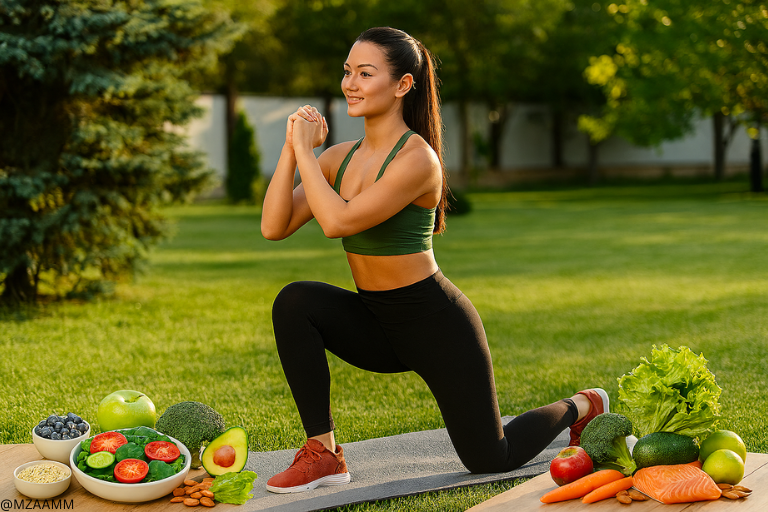
Effective Exercises for Fat Loss and Weight Management
The best and ideal exercise includes cardio, weight training, and flexibility work on a routine basis.
Essential Exercise Types
- Four to five days a week of cardiovascular exercise
- Examples: Running, cycling, swimming, brisk walking.
- Benefits: improve heart health and burn calories.
- Three to four days a week of weight training
- Examples: heavy weight lifting and bodyweight exercises.
- Benefits: Builds muscle and burn extra calories and fat
- Two to three days a week of HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training)
- This is a time-efficient workout. Improve blood pressure and blood sugar level.
- Benefits: The best exercise to burn maximum fat in minimum time.
- Recovery and Flexibility (two days per week)
- Body stretching exercises, Pilates and yoga.
- Benefits: Support muscle recovery and less chance of muscle injury.
📊 Comprehensive Daily Nutrition Table
Summary of Food Groups and Associated Health Benefits
This section presents a recommended allocation of primary food groups within a well-balanced diet. Included are representative examples, ideal daily portion guidelines, and a summary of the distinct health benefits provided by each category.
| Food Group | Examples | %age of Total Caloric Intake | Suggested Daily Servings | Health Benefits |
| Protein | Chicken, fish, tofu, eggs | 30% | 2–3 servings | Facilitates muscular development and supports optimal metabolic function. |
| Carbohydrates | Oats, quinoa, sweet potato | 40% | 3–4 servings | Provides essential calories, dietary fiber, and nutrients critical for sustained energy and digestive health. |
| Healthy Fats | Nuts, olive oil, avocado | 20% | 2–3 servings | Contributes to hormonal regulation and promotes cardiovascular health. |
| Fruits & Vegetables | Berries, greens, carrots | 10% | 4–5 servings | Supplies vital micronutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants necessary for overall well-being. |
The inclusion of each major food group is integral to a nutritionally sound diet, ensuring the provision of key nutrients, supporting physiological functions, and fostering enduring health through balanced consumption. Check Gluten Free Deserts

📈 Chart 1: Ideal Food Intake Distribution
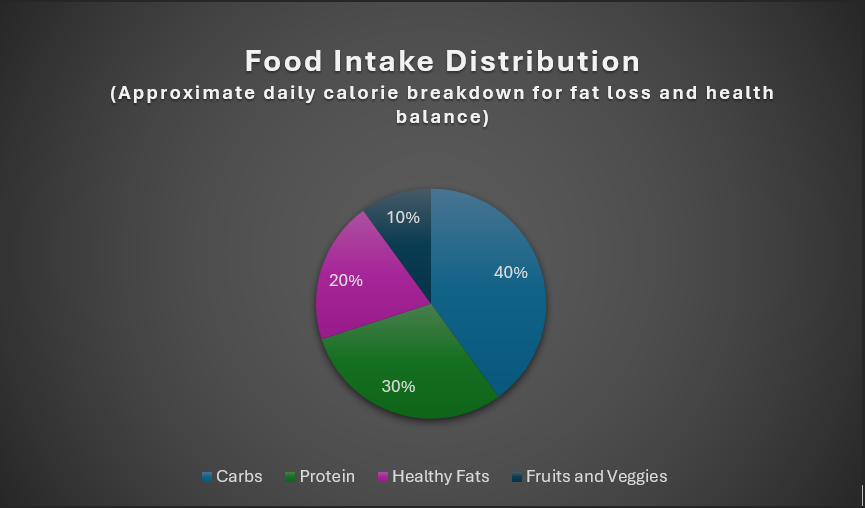
Carbs: 40% Protein: 30% Healthy Fats: 20% Fruits & Vegetables: 10%
📉 Chart 2: Fat Loss Progress (Example Over 12 Weeks)
Overview
The table below outlines the key milestones achieved over the course of the 12-week weight loss journey. Each entry highlights both quantitative changes in weight and body fat percentage, as well as qualitative notes that provide context to the progress made at each stage. Try our quick bread recipe
| Week | Weight (kg) | Body Fat % | Notes |
| 1 | 78 | 25% | At the outset, the starting point is marked by a body weight of 78 kg and a body fat percentage of 25%. |
| 4 | 75.5 | 23% | By week 4, regular workouts combined with dietary adjustments lead to noticeable progress, reflected in reduced weight and body fat. |
| 8 | 73 | 20% | At the 8-week mark, improved endurance is evident, alongside continued reduction in weight and body fat percentage. |
| 12 | 70.5 | 18% | After 12 weeks, visible muscle definition is achieved, signifying a transformation in both physique and body composition. |
Visual representation:
Estimated Weight Reduction Over a Twelve-Week Period
The following chart illustrates the anticipated progress in weight reduction across a 12-week period. The data reflect consistent improvements at regular intervals, corresponding to a structured fitness and nutrition plan.
| Week | Weight (kg) | Progress Indicator |
| 1 | 80 | |█ |
| 4 | 78 | |███ |
| 8 | 76 | |████ |
| 12 | 74 | |█████ |
The visual representation above demonstrates a steady decrease in weight at weeks 1, 4, 8, and 12, moving from 80 kg down to 74 kg. Each bar indicates incremental progress, emphasizing the importance of sustained effort over time for effective weight loss results.

Key Points
Fat loss always starts with a calorie deficit.
To lose fat, make sure you eat fewer or less calories than your body burns so it will use stored fat for energy. Always try to keep your calorie deficit moderate (about 250–750 kcal per day). This process or approach helps you lose fat steadily while maintaining muscle and keeping your energy levels up.
Protein always play an essential role during fat loss journey by helping to maintain muscle, boosting feelings of fullness, and helping recovery.
A practical target is about 1.6–2.4 g/kg bodyweight; in the example table I used 2.0 g/kg.
Weight or Strength training helps maintain or build muscle during fat loss—combine with enough protein. Always do 2-4 sessions per week using progressive overload.
Cardio helps boost calorie burning and supports heart health, but it doesn’t maintain muscle as well as resistance training. It’s best used alongside other exercise types, for example by doing 2 to 4 moderate-intensity sessions or combining steady-state cardio with intervals.
Consuming a wide range of whole foods—such as vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats—ensures you get enough micronutrients, fiber, and fluids. If your diet is limited, consider taking a multivitamin. Also, managing your sleep and stress levels greatly affects your appetite, recovery, and ability to stick to healthy habits over time. Try our Russian Salad
Actionable bullet points
- Multiply your weight in kg by 30 for a maintenance calorie estimate then subtract 250–500 kcal per day to lose fat gradually.
- Recommended protein intake: approximately 1.6–2.4 g/kg body weight (utilise the higher range for individuals with low body fat or those engaging in intensive training).
- Maintain fat intake at 20–35% of calories for hormone health; use carbs to fill the rest.
- Focus on compound lifts (squat, deadlift, press, rows) 2–4 times weekly; add 2–3 cardio sessions if needed.
- Monitor progress by recording body weight in addition to at least one supplementary metric, such as body measurements, garment fit, or weekly photography.
- If your progress slows down while maintaining a long-term calorie deficit, periodically increasing your calories or including refeed days can support hormonal balance and help you stick to your plan.
- Get 7–9 hours of sleep and control stress to aid appetite and recovery.
- Consult a healthcare professional if you have medical conditions or take medication before starting a large deficit.
Macronutrient table (for an 80 kg person; protein = 2.0 g/kg)
I created a table and interactive view showing three typical daily calorie targets. Here’s a summary of what’s displayed: Try our Hydrating Drinks
| Daily kcal | Protein (g) | Protein (kcal) | Fat (g) | Fat (kcal) | Carbs (g) | Carbs (kcal) |
| 1500 | 160.0 | 640.0 | 41.7 | 375.0 | 121.3 | 485.0 |
| 1800 | 160.0 | 640.0 | 50.0 | 450.0 | 127.5 | 710.0 |
| 2200 | 160.0 | 640.0 | 61.1 | 550.0 | 252.5 | 1010.0 |
Notes on the table:
- Protein is set at 2.0 g/kg, which equals 160 grams; therefore, protein calories are calculated as 160 × 4 = 640 kcal.
- Fat is 25% of total calories; the rest are carbs.
- This is just one example; adjust fat and carbs based on your preferences.

📉Chart: projected weight loss over 12 weeks (approximation)
I made a 12-week cumulative projection based on 7,700 kcal ≈ 1 kg body fat, comparing three daily deficits in the chart.
- 250 kcal/day → ~0.9 kg in 12 weeks
- 500 kcal/day → ~5.5 kg in 12 weeks (note: that’s ~0.45 kg/week)
- 750 kcal/day → ~8.2 kg in 12 weeks
| Calorie Deficit (kcal/day) | Weight Loss (kg) in 12 weeks | Notes |
| 250 | ~0.9 | |
| 500 | ~5.5 | ~0.45 kg/week |
| 750 | ~8.2 |
Quick interpretation & practical recommendation for Fat loss
- A daily 300–600 kcal deficit combined with high protein intake and resistance training supports lasting fat loss while maintaining muscle.
- Large deficits (≥750 kcal/day) speed up weight loss but raise the risk of muscle loss, poor training, and adherence problems.
- Every 2–4 weeks, reassess with both scale and non-scale measures; modify calories or training if needed.
| Deficit Size | Protein Intake | Training Type | Fat Loss | Muscle Maintenance | Risks | Assessment Frequency | Assessment Methods | Modification Guidance |
| 300–600 kcal/day | High | Resistance training | Supports lasting fat loss | Maintains muscle | Every 2–4 weeks | Scale and non-scale measures | Modify calories or training if needed | |
| ≥750 kcal/day | Speeds up weight loss | Muscle loss, poor training, adherence problems |

🧩 Summary of Strategy
- Avoid processed food, deep fried items, sugary items, only eat fresh and health food
- Always intake “300-500 kcal/day” less calories from required calories on a daily basis.
- A combination of strength and cardio exercises on a daily basis is very important.
- Sleep daily for at least 7 to 8 hours and do not take stress.
- Track your progress after every 2 weeks; not only weight, also check measurements.
Important: Safety & Personalization
This advice is meant to be general. If you have health issues, are pregnant, breastfeeding, younger than 18, or take medications, consult a healthcare provider before making major changes to your diet or exercise routine.






PHSuperlinklogin? Ayos! Login process was smooth as butter, no annoying hassle. That’s a big plus in my book. Makes getting to the good stuff easy. Go give it a try: phsuperlinklogin
Apaldologin makes it super easy to jump into the games. The site is clean and runs smoothly. Definitely worth checking out if you’re looking for a new spot to play. Login now at apaldologin.
Looking for a good sv288 agent. Any recommendations from you guys?
need a video? video studio in milan offering full-cycle services: concept, scripting, filming, editing and post-production. Commercials, corporate videos, social media content and branded storytelling. Professional crew, modern equipment and a creative approach tailored to your goals.
Продажа тяговых https://faamru.com аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков, ричтраков, электротележек и штабелеров. Решения для интенсивной складской работы: стабильная мощность, долгий ресурс, надёжная работа в сменном режиме, помощь с подбором АКБ по параметрам техники и оперативная поставка под задачу
Продажа тяговых https://ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
Все актуальные адреса здесь на кракен тут ссылка рабочая сегодня для безопасного входа на маркетплейс
Продажа тяговых ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
Hey there. Took a peek at ketquasoxo recently – good design. Standard stuff for the most part, but it seems to work well with no glitches so far. Consider testing it at ketquasoxo.
хороші новинки кіно онлайн підбірка кращих фільмів на вихідні
Just gotta say, jjwincom has been treating me right. Good selection of games, and I even managed to snag a little win the other day. I’m feeling lucky jjwincom
Нужен детейлинг leveldetailingcy специализированный детейлинг центр на Кипре в Лимассоле, где заботятся о безупречном состоянии автомобилей, предлагая клиентам полный комплекс услуг по уходу за транспортными средствами. Мастера студии с вниманием относятся к каждой детали: они не только выполняют оклейку кузова защитными материалами, но и проводят тщательную обработку салона, возвращая автомобилю первозданный вид.
Do you want bonuses? https://www.reddit.com/r/referralcodes/comments/1pjpsi1/csgofast_promocode_for_2026/ deposit bonuses, free cases, terms and conditions. A quick activation guide, FAQ, and the latest updates.
Делаешь документы? https://datadoc.ru/ позволяет существенно ускорить работу: с его помощью вы сможете готовить необходимые документы в десять раз быстрее и при этом гарантированно избегать ошибок. Инструмент предельно прост в освоении — специальное обучение не требуется. Все ваши данные надёжно защищены, а настройка индивидуальных шаблонов выполняется оперативно и без сложностей.
Rebricek najlepsich kasin https://betrating.sk/casino-hry/automaty-online/dracula/ na Slovensku: bezpecni prevadzkovatelia, lukrativne bonusy, hracie automaty a zive kasina, pohodlne platby a zakaznicka podpora. Cestne recenzie a aktualizovane zoznamy pre pohodlne online hranie.
SEO-продвижение сайта https://seo-topteam.ru в Москве с запуском от 1 дня. Экспресс-анализ, приоритетные правки, оптимизация под ключевые запросы и регион. Работаем на рост позиций, трафика и лидов. Подходит для бизнеса и услуг.
Тяговые аккумуляторные https://ab-resurs.ru батареи для складской техники: погрузчики, ричтраки, электротележки, штабелеры. Новые АКБ с гарантией, помощь в подборе, совместимость с популярными моделями, доставка и сервисное сопровождение.
Продажа тяговых АКБ https://faamru.com для складской техники любого типа: вилочные погрузчики, ричтраки, электрические тележки и штабелеры. Качественные аккумуляторные батареи, долгий срок службы, гарантия и профессиональный подбор.
дивитися найкращі фільми 2025 класика кінематографа онлайн
Онлайн курсы психологии https://ilmacademy.com.ua удобный формат обучения для тех, кто хочет освоить профессию психолога, получить практические навыки и пройти профессиональное обучение дистанционно. Курсы подойдут для начинающих и специалистов, ориентированных на практику.
Свежие новости https://arguments.kyiv.ua Украины и мира: события в Киеве и регионах, экономика, общество, происшествия, спорт, технологии и культура. Оперативная лента 24/7, аналитика, комментарии, фото и видео.
Всё для женщин https://glamour.kyiv.ua в одном месте: тренды моды и бьюти, здоровье, питание, спорт, семья, дети, отношения и саморазвитие. Статьи, чек-листы, идеи и обзоры, которые помогают принимать решения и чувствовать себя увереннее.
Портал для женщин https://woman24.kyiv.ua про жизнь без лишнего: красота, женское здоровье, питание, рецепты, уютный дом, финансы, работа и отдых. Практичные советы, честные обзоры и вдохновляющие истории.
Медицинский портал https://medicalanswers.com.ua для пациентов: здоровье, диагностика, лечение, профилактика и образ жизни. Экспертные статьи, справочник симптомов, советы специалистов и актуальные медицинские новости. Достоверная информация в одном месте.
Новостной портал https://ua-novosti.info Украины без лишнего: оперативная лента, репортажи из областей, интервью и разборы. Политика, финансы, социальные темы, медицина, образование, IT. Фото/видео, инфографика, уведомления и топ-материалы дня.
Всё о здоровье https://medfactor.com.ua на одном медицинском портале: болезни и их лечение, анализы, препараты, обследования и профилактика. Материалы подготовлены с опорой на клинические данные и врачебную практику. Читайте онлайн в любое время.
Главные события https://vesti.in.ua Украины — коротко и понятно. Мы собираем новости из Украины и мира, проверяем данные и даём ясные объяснения. Подборки по темам, новости городов, аналитика, мнения, видео. Обновления каждый час, удобно на смартфоне.
Электронные компоненты https://zener.ru с прямыми поставками от производителей: микросхемы, пассивные элементы, разъёмы и модули. Гарантия оригинальности, стабильные сроки, выгодные цены и подбор под ТЗ. Поставки для производства, сервиса и разработки.
Нужен дизайн? design studio создаем функциональные и стильные пространства для квартир, домов и офисов. Планировки, 3D-визуализации, подбор материалов и авторский надзор. Индивидуальный подход, реальные сроки и продуманные решения под ваш бюджет.
Онлайн-портал https://avian.org.ua для строительства и ремонта: от фундамента до отделки. Подбор материалов, пошаговые гайды, сравнение технологий, советы мастеров и актуальные цены. Полезно для застройщиков, подрядчиков и частных клиентов.
Женский портал https://replyua.net.ua про красоту и заботу о себе: уход, макияж, волосы, здоровье, питание, спорт, стиль и отношения. Практичные советы, чек-листы, подборки и вдохновляющие истории. Читайте онлайн и находите идеи на каждый день.
Строительный портал https://ateku.org.ua о ремонте и строительстве: технологии, материалы, сметы, проекты домов и квартир, инструкции и советы экспертов. Обзоры, калькуляторы, нормы и примеры работ — всё для частного и коммерческого строительства.
Всё о строительстве https://hydromech.kiev.ua и ремонте в одном месте: материалы, технологии, дизайн, инженерия и безопасность. Экспертные статьи, инструкции, калькуляторы и кейсы. Помогаем планировать работы и экономить бюджет без потери качества.
Женский журнал https://asprofrutsc.org онлайн: тренды бьюти и моды, лайфхаки для дома, рецепты, материнство, карьера и финансы. Экспертные материалы, понятные инструкции и идеи, которые можно применить сразу. Обновления ежедневно, удобная навигация.
Портал для строителей https://inter-biz.com.ua и заказчиков: советы по ремонту, обзоры материалов, расчёты, сметы и технологии. Реальные кейсы, чек-листы и рекомендации специалистов для надежного результата на каждом этапе работ.
Портал для женщин https://beautyrecipes.kyiv.ua про гармонию и результат: здоровье, красота, стиль, саморазвитие, семья и отношения. Обзоры косметики и процедур, планы питания, тренировки, советы по дому и вдохновляющие истории. Всё в одном месте, 24/7.
Performance reporting transparency builds confidence in best crypto signals providers. Monthly reports detailing all trades, win rates, average returns, and maximum drawdowns enable objective service evaluation beyond marketing claims.
Туристический портал https://atrium.if.ua о путешествиях: направления, отели, экскурсии и маршруты. Гайды по городам и странам, советы туристам, визы, билеты и сезонность. Планируйте поездки удобно и вдохновляйтесь идеями круглый год.
Женский медиа-портал https://abuki.info про вдохновение и практику: тренды красоты, идеи образов, забота о теле, эмоциональное равновесие, материнство и быт. Подборки, гайды и понятные советы, которые легко применять каждый день.
Мужской портал https://realman.com.ua про жизнь и эффективность: здоровье, сила и выносливость, карьера, инвестиции, стиль и отношения. Экспертные материалы, обзоры и чек-листы. Читайте онлайн и применяйте на практике.
Онлайн авто портал https://necin.com.ua о новых и подержанных автомобилях: каталоги моделей, рейтинги, отзывы владельцев и экспертные обзоры. Новости рынка, технологии, электромобили и полезные сервисы для выбора авто.
Авто портал https://bestsport.com.ua для водителей и автолюбителей: обзоры и тест-драйвы, сравнение моделей, характеристики, цены и новости автопрома. Советы по покупке, эксплуатации и обслуживанию автомобилей. Всё об авто — удобно и понятно.
Всё о туризме https://hotel-atlantika.com.ua и отдыхе в одном месте: направления, визы, транспорт, отели и развлечения. Путеводители, маршруты, обзоры и советы опытных путешественников. Удобно планировать поездки онлайн.
Онлайн-портал https://deluxtour.com.ua для путешественников: куда поехать, что посмотреть, где остановиться и как сэкономить. Маршруты, подборки, отзывы, карты и полезные сервисы. Актуальная информация для самостоятельных поездок и отдыха.
Портал для строителей https://rvps.kiev.ua и заказчиков: ремонт, строительство, сметы и проекты. Обзоры материалов, расчёты, чек-листы и советы специалистов, которые помогают планировать работы и экономить бюджет.
Портал для туристов https://inhotel.com.ua и путешественников: гайды по странам, маршруты, достопримечательности и события. Практичные советы, карты, подборки и идеи для отпуска, выходных и активных путешествий.
Ландшафтный дизайн https://kinoranok.org.ua ремонт и строительство под ключ: проектирование участков, благоустройство, озеленение, дорожки, освещение и малые архитектурные формы. Комплексные роботы для частных и коммерческих объектов с гарантией качества.
Автомобильный портал https://livecage.com.ua тест-драйвы, сравнения, комплектации, безопасность и экономичность. Актуальные новости, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию, рекомендации для начинающих и опытных водителей.
Всё про автомобили https://sedan.kyiv.ua в одном портале: каталог авто, обзоры и рейтинги, новости автопрома и советы экспертов. Покупка, эксплуатация, сервис и тренды — полезная информация для каждого водителя.
Компания BritishSchool https://britishschool.kiev.ua профессиональные тренинги, семинары и курсы для детей и взрослых. Обучение с опытными преподавателями, современные методики, практические навыки и уверенный результат. Онлайн и офлайн форматы.
Портал о строительстве https://repair-house.kiev.ua и ремонте без лишней теории: практические советы, обзоры материалов, расчёты, инструменты и этапы работ. Помогаем планировать проекты, контролировать качество и экономить бюджет.
Проблемы с алкоголем? вывод из запоя на дому цены помощь врача, детоксикация, стабилизация состояния и наблюдение. Конфиденциально, без постановки на учет, с учетом возраста и сопутствующих заболеваний.
Ищешь казино? рейтинг лучших онлайн казино на деньги онлайн лицензия, бонусы, выплаты, игры и отзывы игроков. Сравниваем условия, безопасность и удобство, чтобы помочь выбрать надежное казино для игры онлайн.
Нужны блины и диски? блины для штанги от производителя широкий выбор весов, надежные материалы, точная калибровка. Отличное решение для силовых тренировок, кроссфита и профессиональных спортзалов.
Мультимедийный интегратор itec интеграция мультимедийных систем под ключ для офисов и объектов. Проектирование, поставка, монтаж и настройка аудио-видео, видеостен, LED, переговорных и конференц-залов. Гарантия и сервис.
сервис рассылки подключить https://email-rassylka.ru
code bonus melbet melbet apk
Нужен проектор? https://projector24.ru большой выбор моделей для дома, офиса и бизнеса. Проекторы для кино, презентаций и обучения, официальная гарантия, консультации специалистов, гарантия качества и удобные условия покупки.
ремонт и химчистка обуви химчистка обуви
люстры светильники сделать деревянную люстру
https://mhp.ooo/
Лучшее казино upx играйте в слоты и live-казино без лишних сложностей. Простой вход, удобный интерфейс, стабильная платформа и широкий выбор игр для отдыха и развлечения.
Лучшее казино ап икс сайт играйте в слоты и live-казино без лишних сложностей. Простой вход, удобный интерфейс, стабильная платформа и широкий выбор игр для отдыха и развлечения.